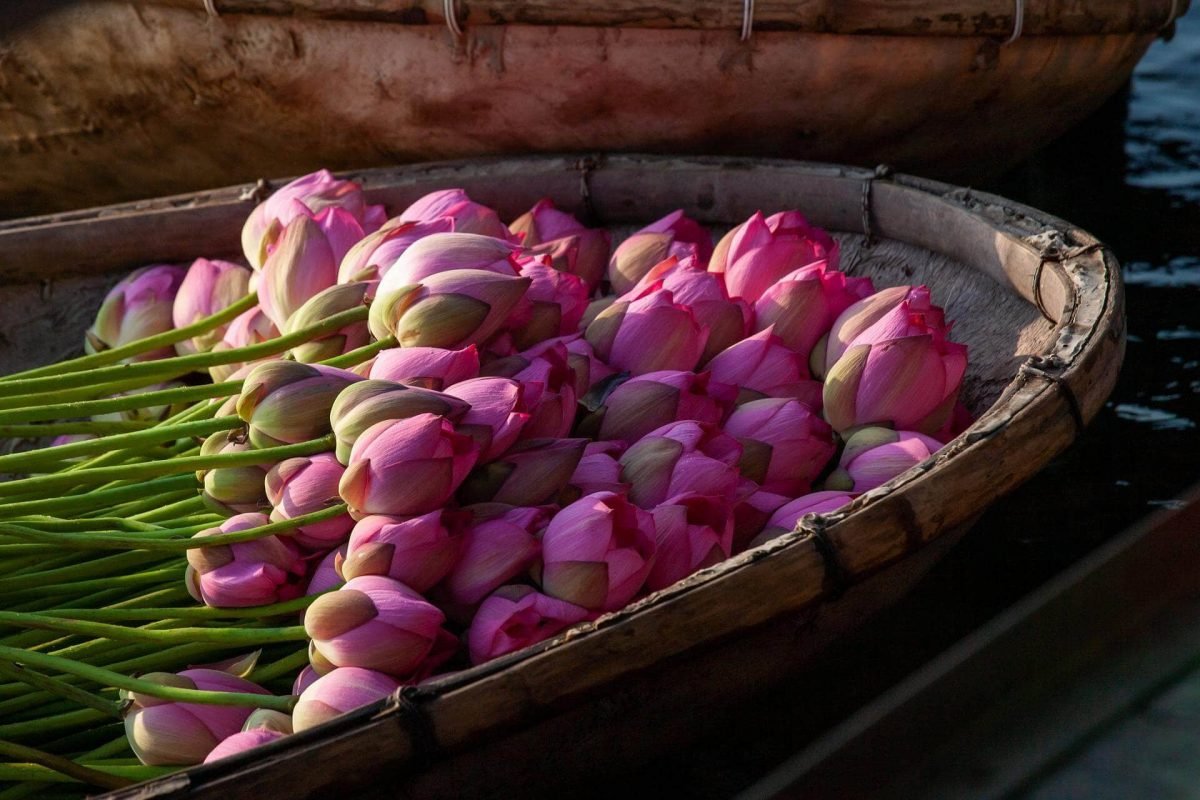
Lotus is scientifically known as Nelumbo nucifera. It’s also called sacred lotus and Indian lotus.
It’s cultivated in many parts of the world but especially in Asia, including India and Southeast Asia. It grows in water and is often confused with water lilies, featuring a bowl shape with petals and green leaves. Its flowers can be white, pink, red, or blue.
Lotus is available in many preparations, including dried root, teas, powders, capsules, and extracts.
Today, it’s studied for its possible health benefits. Researchers are particularly interested in the plethora of beneficial compounds found in the plant, including flavonoids and alkaloids (4).
1. Has antioxidant properties
The lotus plant contains many flavonoid and alkaloid compounds that may act as antioxidants (4).
Antioxidants help neutralize reactive molecules known as free radicals. If free radicals build up in your body, they can cause oxidative stress, which damages cells and contributes to disease development.
Some of the antioxidant compounds in lotus include kaempferol, catechin, chlorogenic acid, and quercetin. The antioxidant activity of lotus appears to be most concentrated in its seeds and leaves
While there’s limited research on the human health effects of consuming lotus, it’s thought that these antioxidant compounds might protect against diseases that stem from oxidative stress.
In particular, they may have anticancer effects, protect against Alzheimer’s disease, and prevent liver damage.
One test-tube study found that the leaves, petals, and stamen — the pollen-producing part of the plant — had strong antioxidant activity and inhibited enzymes involved in Alzheimer’s disease.
2. Acts as an antibacterial agent
Lotus has been studied for its antibacterial effects, including against bacteria in your mouth.
How lotus exhibits antibacterial properties is not clear, but the many beneficial compounds it contains likely play a role.
Studies suggest that lotus leaf extract can fight bacterial species that cause cavities and gum infections. Thus, it has potential as an ingredient in toothpaste and other oral hygiene products.
However, it’s important to note that these studies were conducted in test tubes. Research in humans is needed to better understand the potential of using lotus to treat oral infections.
The bottom line
The lotus plant has a long history of use in Asian cuisine and traditional medicine.
It contains many compounds that exhibit health benefits, including antioxidant and antibacterial effects. However, more research is needed to better understand how consuming parts of this plant or its supplements may benefit human health.
If you’re curious about trying a lotus supplement, discuss it with a healthcare professional first, as the safety and side effects of doing so remain largely unknown. That said, using lotus in cooking is generally considered safe.